Really honest. Good communication. Good outcomes.
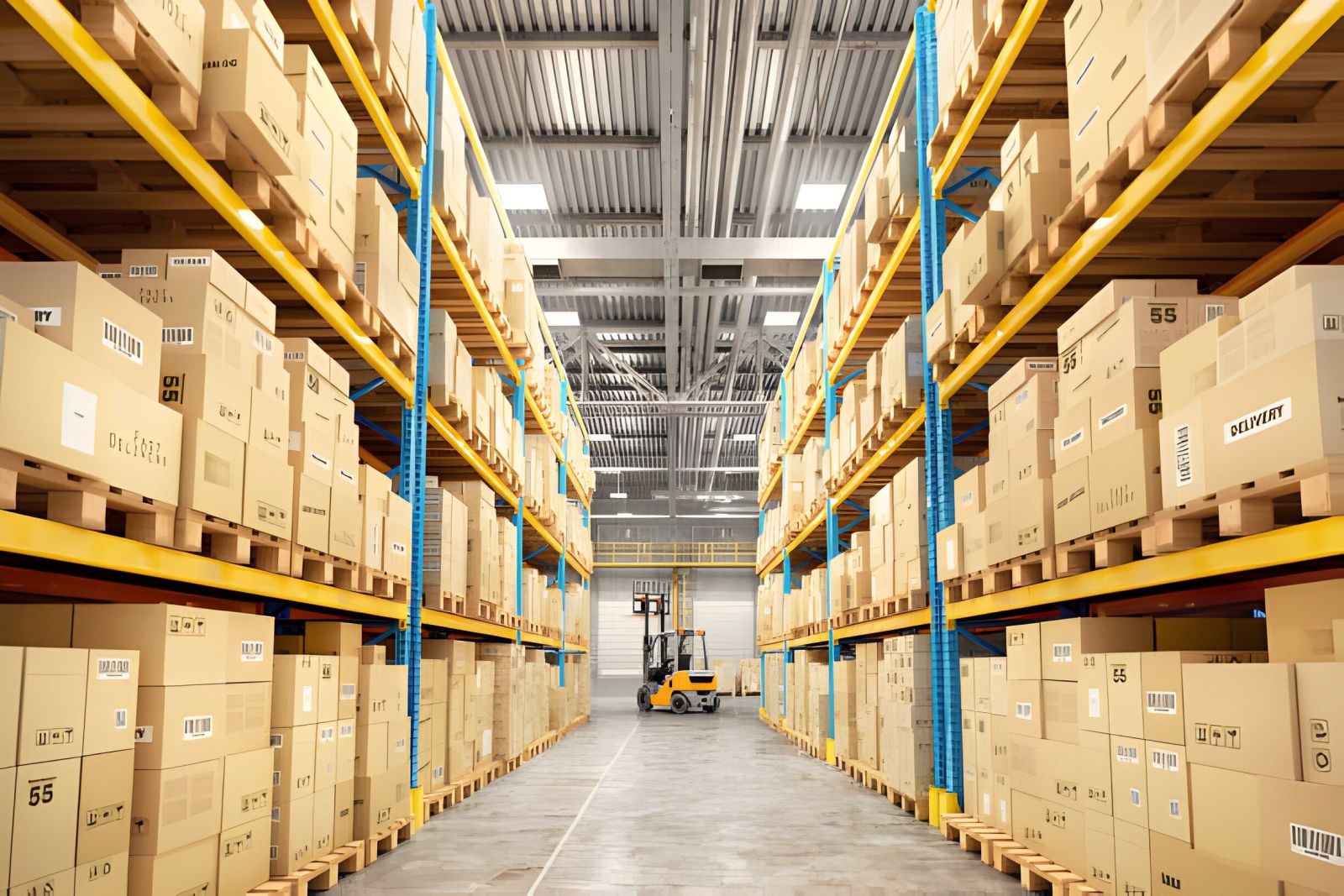

Warehouse racking plays a critical role in the efficient storage management of businesses. These systems are designed to maximize space utilization, enhance inventory management, and improve overall logistics. By providing structured storage, industrial racking helps in organizing products systematically, allowing for easy access and retrieval.
In this article, we will explore different types of industrial racking systems that are commonly used in warehouses. Understanding their unique characteristics, advantages, and suitable applications will help you make informed decisions for your storage needs.
Here are some of the most commonly used industrial racking systems:
Whether you're looking to optimize space or streamline your inventory processes, this guide provides valuable insights into various racking solutions tailored to different business requirements.
Selective Racking is the most common type of industrial racking system used in warehouses. It provides direct access to each pallet, making it highly adaptable and customizable for various storage needs.
Selective Racking consists of upright frames, horizontal beams, and connectors. Pallets are stored on horizontal beams, which are adjustable to accommodate different pallet sizes and weights.
Industries such as retail, distribution centers, and manufacturing benefit from Selective Racking due to its flexibility and ease of access. For example:
Consider Selective Racking if your warehouse requires:
Evaluating these factors helps determine if Selective Racking aligns with your operational needs.
Double Deep Racking is a storage solution that offers higher storage density without compromising selectivity. It allows for pallets to be stored two rows deep, effectively doubling the storage capacity within the same space compared to Selective Racking.
Double Deep Racking involves placing one pallet behind another in a single slot, requiring specialized handling equipment like double-deep reach trucks for access. Unlike Selective Racking, where each pallet is immediately accessible, Double Deep Racking prioritizes higher storage density.
Industries such as food and beverage, retail, and manufacturing often utilize Double Deep Racking for its balance of accessibility and increased storage density. For example, a beverage distribution center may benefit from this system to store large quantities of similar products efficiently.
Assessing if Double Deep Racking fits your business needs involves considering factors like:
By evaluating these aspects, you can determine if Double Deep Racking aligns with your warehouse operations and storage requirements.
Drive-in/drive-through racking is an innovative solution for high-density storage, utilizing either Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) or First-In-First-Out (FIFO) inventory management systems.
To determine if this system aligns with your warehouse operations:
Using these guidelines will help determine if drive-in/drive-through racking meets your specific business needs.
.jpg)
Pallet flow racking is a dynamic storage solution that uses inclined roller beds or wheels to move pallets from the loading end to the picking face using gravity. This system ensures efficient First-In-First-Out (FIFO) inventory control by automatically rotating stock.
The core components of pallet flow racking are:
Implementing pallet flow racking can lead to significant efficiencies:
Despite its advantages, there are certain limitations:
This racking system finds its niche in specific environments:
To determine if pallet flow racking suits your facility, consider:
By understanding these elements, you can better gauge whether pallet flow racking aligns with your operational needs and warehouse conditions.
Push Back Racking uses sloping rails and nested carts to create compact storage that is still easy to reach for multiple pallets with different products. Unlike other types of racking, this design allows for the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) method of inventory management, which is perfect for businesses with moderate product turnover.
This type of racking is commonly used in:
When deciding whether Push Back Racking is suitable for your warehouse, take into account factors such as how quickly your inventory turns over and your need for space optimization. This system works best in situations where you require dense storage and fast access to various products.
Cantilever racking is a specialized solution designed for the storage of long, bulky items such as lumber, pipes, or furniture. This system is characterized by its unique arm-based design, which offers several advantages:
Cantilever racking comes in two main configurations:
To determine if cantilever racking fits your warehouse needs, consider:
Exploring additional specialized racking systems enhances your understanding of warehouse optimization. These systems cater to unique storage requirements and operational efficiencies:
Designed for maximum space utilization, VNA racking narrows the aisle width to accommodate specialized forklifts. This system is ideal for high-density storage environments where maximizing floor space is crucial.
Also known as mobile racking, compact racking involves a series of racks mounted on mobile bases that can be moved along rails. This system eliminates the need for multiple aisles, significantly increasing storage capacity.
Utilizing gravity-driven mechanisms, live pallet racking systems enable automatic stock rotation. Ideal for FIFO inventory management, these are often used in temperature-controlled environments like cold storage or distribution centers with high turnover rates.
Mobile racking allows entire rows of shelving to move along floor tracks, creating a flexible and dynamic storage solution. This system is particularly effective in warehouses with variable storage needs and limited space.
Understanding these specialized systems helps you tailor your warehouse strategy to specific operational demands, enhancing both efficiency and productivity.
Choosing the right industrial racking system is crucial for optimizing your warehouse storage and ensuring smooth operations. Carefully evaluate your specific needs, such as load capacity, inventory turnover, and available space, to make an informed decision.
While the types of racking systems discussed in this article are widely used, consulting with a professional can provide personalized advice tailored to your warehouse layout and design. This ensures that you maximize efficiency and safety.
Explore our range of industrial racking solutions to find the perfect fit for your warehouse needs. Make a choice that aligns with your operational goals and sets you up for long-term success.
Selective Racking is the most common type of industrial racking system, consisting of upright frames and horizontal beams to store a wide range of products.
Selective Racking offers versatility and easy adjustability to store various products, making it suitable for industries such as retail, distribution centers, and manufacturing.
Double Deep Racking involves placing one pallet behind another to maximize warehouse space by doubling the storage capacity.
Drive-in/Drive-through Racking enables deep stacking and efficient space utilization while minimizing aisle space, making it suitable for industries like food and beverage.
Push Back Racking uses sloping rails and nested carts to create a dynamic storage solution, increasing picking face capacity by storing pallets deep within the racks.
The cantilever rack offers versatility in storing items of varying lengths and weights, making it ideal for industries like construction

Design

Manufacture

Deliver
Install
Beginning as a sketch on our product designer’s table, each and every one of our products have been passed through multiple hands, from designers to engineers to quality experts. We design fixtures and shop fittings specifically for retail purposes, all with the purpose of maximising the potential profits of our clients. Our origins date back to G.H. Burton Metalworks who began trade in 1953, fabricating metal shopfittings and fixtures for renowned clients such as Bunnings. We pride ourselves on a timely and unproblematic manufacturing and distribution service. We will assist you with any enquiries you may have; our knowledgeable customer service, sales and delivery teams will save you time and money on your next store project, Australia wide.
Really honest. Good communication. Good outcomes.
This has really improved the flow of our store.
We certainly met our goals with retail fixtures.